Items from pit tombs
The pit tombs in the Phoenician necropolis of Monte Sirai, mainly used with the cremation ritual, are the oldest types of burial documented so far for the Phoenician and Punic settlement, between the end of the 7th century B.C. and the next century.

Fig. 1 - The area of the Phoenician necropolis (highlighted) photo Unicity S.p.A.;
The ceramic items, sometimes painted red, included jugs with mushroom brims and lobed lips, in several variations (figs 2-4). Plates - often painted - cups and oil lamps have also been found. The items include decorative items and items to ward off evil: jewels, amulets and scarabs. Relations with the Greek work are documented by the presence of ceramic items from the Ionia and Corinth regions. A sign of relations with people from the territory are the Nuragic pottery items (fig. 3).

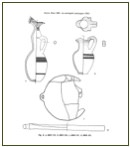
Figs. 2-3 - Findings from Phoenician necropolis (GUIRGUIS 2012, tab. 17); ceramic designs from tomb 32 (below Nuragic pot): BARTOLONI 1983, fig. 11.

Fig. 4 - Items from tomb 292 (GUIRGUIS 2013, fig. 40).
Bibliografia
- P. BARTOLONI, La necropoli (campagna 1982), in RStudFen, XI, pp. 205-221.
- M. GUIRGUIS, Monte Sirai 2005-2010. Bilanci e prospettive, in Vicino & Medio Oriente, 16, pp. 51-82.
- M. GUIRGUIS, Monte Sirai 1963-2013 mezzo secolo di indagini archeologiche, Sassari.

 VR
VR